Chapter 1: First Farmers
Choose the correct alternative and write the complete sentence.
‘Yellow River’ is the English translation of the Chinese name ______.
OPTIONS
Kemet
Mother
Sorrow
Huang He
SOLUTION
‘Yellow River’ is the English translation of the Chinese name Huang He.
The Australian archaeologist ______ coined the term ‘Neolithic Revolution’.
OPTIONS
Gorden Willey
Gorden Childe
Herodotus
Collingwood
SOLUTION
The Australian archaeologist Gorden Childe coined the term ‘Neolithic Revolution’.
The neolithic people at Gilgal had systematically planted ______ trees.
OPTIONS
Guava
Sapodilla
Fig
Indian blackberry
SOLUTION
The neolithic people at Gilgal had systematically planted Fig trees.
______ in the Shirur taluka of Pune district, is an important site of the village of Chalcolithic farmers in Maharashtra.
OPTIONS
Saradwadi
Ranjangaon
Pabal
Inamgaon
SOLUTION
Inamgaon in the Shirur taluka of Pune district is an important site of the village of Chalcolithic farmers in Maharashtra.
Find the incorrect pair from set B and write the correct ones.
SOLUTION
Complete the concept map.
SOLUTION
Explain the following statement with reasons.
The camps of Mesolithic people developed into the first settled villages of neolithic people in Mesopotamia.
SOLUTION
Mesopotamia is between the two rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates.
The Mesolithic people began to settle in the region (Mesopotamia) for a longer time, due to the availability of ample water.
As both the rivers flooded annually, fertile soil was deposited on their banks.
Ample water and fertile soil resulted in camps of Mesolithic people, who developed into the first settled neolithic villages, which grew wheat and barley.
‘Huang He’ river is considered to be the mother of the Chinese culture.
SOLUTION
The yellow silt brought by the ''Huang He' river, earns her the name of 'Yellow River' in English.
The other names 'River' and 'Mother', indicate her extraordinary place in the Chinese culture.
The name 'River' indicates her importance as a river.
The Chinese culture evolved here, with wheat, foxtail millet, and rice being grown by neolithic farmers in the villages.
In the latter half of the neolithic age, pottery-making had become an art that required special skills.
SOLUTION
The neolithic pottery, in the beginning, was in monochrome, i.e., single colour with a burnished surface. Pots were polished by rubbing with a wooden or stone tool.
Some pots had carved designs, using techniques of stamping and applique work.
Gradually Neolithic people began to decorate their pots with painted design.
Thus, in the latter half of the Neolithic age, pottery making had become an art that required special skills.
State your opinion.
There were radical changes in the way of human life during the neolithic age.
SOLUTION
In the neolithic age, people lived settled lives with permanently occupied dwellings.
The common storage places of food-grains indicated that transactions related to food production were centrally controlled.
Hierarchical social and family structure and concept of inheritance have their roots in Neolithic times.
Pottery making along with polished stone tools is an essential characteristic of neolithic culture.
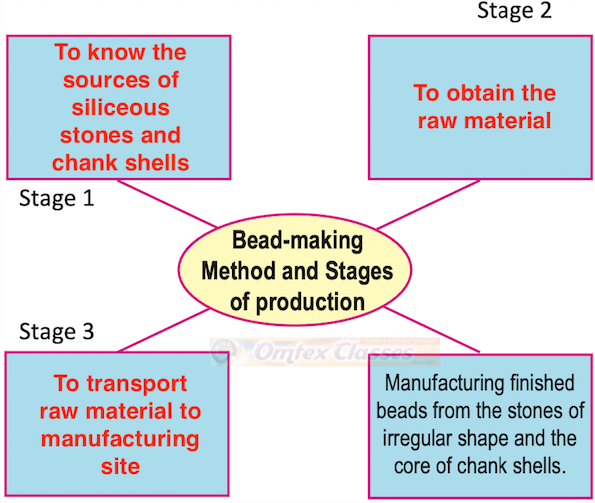
Beads of various types of siliceous stones and chank shells were made, indicating craft specialization and various classes of skilled artisans.
The neolithic people invented wheel and the technology they had developed so far, underwent a revolution.
SOLUTION
Neolithic people produced wheel-made pottery.
Wheel technology made it possible to produce pottery on a large scale.
The invention of the wheel made it possible to obtain the raw material from distant places in lesser time.
It became easier to send the finished goods to distant markets, where it was in more demand.
It helped to develop trade and commerce and transport on a greater scale.
Observe the map and answer the following question based on it.
What is the name of the sea at the north of the African continent?
SOLUTION
The name of the sea at the African continent is Mediterranean Sea.
In which continent did the Harappan civilisation originate?
SOLUTION
The Harappan civilization originated in the Continent of Asia.
What is the name of the ocean at the south of India?
SOLUTION
Indian Ocean is the name of the ocean at the south of India.
Write short notes.
Neolithic ‘Jericho’
SOLUTION
The Palestinian city of J ericho, on the banks of the river Jordan, is the first neolithic permanent settle' in 9000 B.C.E.
It started getting organised into a well-knit society by about 8000 B.C.E.
The village had a protective wall around it, with a watch tower, giving evidence of an organised society.
It is proved that cultivation began in Jericho, as discovered at Gilgal a site near Jericho.
Laboratory analysis have proved that neolithic people had systematically planted fig cuttings.
This stands to be the first attempt of planned cultivation.
‘Holocene’ epoch
SOLUTION
The last glacial period in the history of our planet came to an end about 12000-11000 years ago.
This was the beginning of a new epoch, known as 'Holocene'.
With the beginning of Holocene, glaciers began to melt, increasing volume of water in rivers and oceans.
As a result, availability of animals and vegetation for food increased.
The period witnessed the extinction of gigantic mammoth.
Variety of fishes, small animals like goat, sheep, deer were available for food.
Answer the following question in detail.
Write in detail about the ‘first farmers’ and beginning of agriculture in India.
SOLUTION
Archaeological sites of Neolithic villages, which have been discovered prove that there were well settled villages in the Indian subcontinent, as early, as 8000 B.C.E.
Historian scholars generally agree that the Harappan cities evolved from these early villages.
Barley was the main crop grown by the farmers in these villages, where wheat was grown on smaller scale.
The farmers in these villages were the 'first farmers' of the Indian Sub-continent. They lived in mud houses and domesticated cattle and goat-sheep.
The transition from hunter-gatherer's life to the beginning of cultivation spans through 10000- 8700 B.C.E.
The beginning of cultivation is also the beginning of Neolithic age. The period also marked domestication of animals along with cultivation.
While wheat and fiaxseeds were grown, barley was the main crop in this period.
Modified composite tools like fishing harpoons, spears and arrows were made. Blades known as microliths and tools like sickle and scythe were used for harvesting cereals and fruits.
What knowledge was essential for the neolithic people to make pottery?
SOLUTION
The neolithic pottery, in the beginning, was in monochrome (single colour) with a burnished i.e., polished by running with a wooden or stone tool, surface. Some pots had carved designs.
The techniques of stamping and applique work i.e., pasting wet clay ribbons and making patterns on them were also used.
Painted designs on pots in the latter half of the neolithic age, made pottery art that required special skills.
To master the art of pottery-making one needs to possess knowledge of the following things -
(a) To know the source of clay of excellent quality.
(b) To manage to obtain clay.
(c) To knead and prepare the clay for pottery production.
(d) To be able to turn the pot to the desired shape.
(e) To have artistic skill for decorating the pottery.
(f) To know the technique of baking pottery at proper temperatures, approximately 850° - 900° celsius.Pottery helps us to know the cultural history, the material richness of the place, where it was found.
With the help of pottery, we can also know about the contacts of the residents of the place with other cultures.
Write about the trade and transport in the neolithic age.
SOLUTION
In the latter half of the Neolithic age, people had started using beasts of burden for transporting goods.
Tools like axe, scrapers and chisels enabled neolithic people to cut trees and work on wood.
Probably the round-shaped pieces of wooden logs were used as wheels, as they could easily gain momentum.
The neolithic people invented the wheel and the technology they had developed so far underwent a revolution.
The Neolithic people began to produce wheel-made pottery. The wheel technology made it possible to obtain the raw material from distant places in much lesser time.
It became easier to send the finished goods to distant markets where it was more in demand.
It helped to develop trade and transport on a greater scale.
Write about the beginning of urbanisation in the neolithic age.
SOLUTION
After settling down at one place for a long time, a feeling of ownership arose among neolithic people.
This feeling was focused on their individual dwellings and the piece of land cultivated by them.
With social organisation and administration, the villages expanded.
Along with it, awareness of collective landholdings and the village boundaries became prominent.
It was thus felt that the village community had a natural right over the immediate territory around the village periphery.
This kind of awareness of natural right over a particular region is known as 'territoriality'.
Rules and norms were created to manage the collective resources, water sources, crafts dependent on it, trade and community life etc. Consequently, rituals and their details gained importance.
The need for managing and keeping records of trade, rituals, writing, systems and administrative machinery developed.
It gave rise to administrative centres. Such administrative centres attract a large number of population which includes officials, people from various occupations.
Balbharati Solutions for History 11th Standard Maharashtra State Board
• Chapter 2: First Cities of India
• Chapter 3: Chalcolithic Villages in India
• Chapter 5: Janapadas and Republics
• Chapter 6: Second Urbanisation in India
• Chapter 7: India and Iran (Persia)
• Chapter 8: India during Mauryan period
• Chapter 9: Post Mauryan India
• Chapter 11: Kingdoms in South India
• Chapter 12: India, Nations in the northwest of the Indian Subcontinent and China
• Chapter 13: India, Shri Lanka and Southeast Asia
• Chapter 14: Delhi Sultanate, Vijayanagar and Bahamani Kingdom
• Chapter 15: India during Mughal period
• Chapter 16: Swarajya to Empire (Maratha period)
.