Chapter 5: Emerging Modes of Business
Select the correct option and rewrite the sentence.
For Online transactions____________ is required.
registration
trading
business
Solution:
For online transactions, registration is required.
The term 'e-business' is derived from the term ___________ and e-commerce.
Cash
e-pay
Solution:
The term 'e-business' is derived from the term e-mail and e-commerce.
The transactions under ____________ are between consumers and consumers.
B2B
C2C
B2C
Solution:
The transactions under C2C are between consumers and consumers.
The process of contracting a business function to someone else is called as ____________.
outsourcing
trading
e-business
Solution:
The process of contracting a business function to someone else is called outsourcing.
In online shopping customers put the product in the ____________.
shopping mall
shopping cart
shopping bag
Solution:
In online shopping, customers put the product in the shopping cart.
Match the pairs:
Solution:
Give one word/term/phrase for the following sentence.
The stage where the goods bought are delivered to the customer.
Solution:
The stage where the goods bought are delivered to the customer. - Delivery stage
The term derived from the terms of e-mail and e-commerce.
Solution:
The term derived from the terms of e-mail and e-commerce. - e-business
The transaction which is done with the help of the internet.
Solution:
The transaction which is done with the help of the internet.- online transactions
The first step in an online transaction.
Solution:
The first step in an online transaction. - Registration
The process of contracting a business function to specialized agencies.
Solution:
The process of contracting a business function to specialized agencies. - outsourcing
A subset of outsourcing.
Solution:
A subset of outsourcing. - BPO
Sub-segment of BPO
Solution:
Sub-segment of BPO - KPO (Knowledge Process Outsourcing)
One of the value-added BPO service which involves legal work.
Solution:
One of the value-added BPO service which involves legal work. - LPO
State with reasons whether the following statement true or false.
It is easy to set up e-business as compared to traditional business.
True
False
The term e-business is derived from the term e-mail and e-commerce.
True
False
e-business allows you to work across the globe in any field.
True
False
LPO stands for legal product outsourcing.
True
False
KPO requires advanced analytical and technical skills.
True
False
Find the odd one.
BPO
RTO
LPO
KPO
B2B
B2C
A2Z
C2C
Debit card
Credit card
Aadhar card
ATM card
Complete the sentence.
E-business is an abbreviation for____________.
Solution:
E-business is an abbreviation for electronic business.
The term e-business came into existence in the year __________.
Solution:
The term e-business came into existence in the year 1997 .
E-business means using the ___________ to connect people and process.
Solution:
E-business means using the Internet to connect people and process.
E-business is ___________ of e-commerce.
Solution:
E-business is Superset of e-commerce.
E-commerce is ________ of e-business.
Solution:
E-commerce is a Subset of e-business.
The process of contracting a business function to specialized agencies is known as _____________.
Solution:
The process of contracting a business function to specialized agencies is known as Outsourcing.
Select the correct option and complete the table.
(Business to Business, First step, e-commerce, payment mechanism, e-business)
Answer in one sentence.
What is E-business?
Solution:
E-business means using the internet to connect people and process. E-business establishes more closer and responsive relationship with partners, employees, and suppliers.
What is outsourcing?
Solution:
Outsourcing is the process of contracting a business function or any specific business activity to specialized agencies mostly the non-core areas such as sanitation, security, household pantry, etc. are outsourced by the company. The company makes a formal agreement with the agency.
What is Online Transaction?
Solution:
Online transaction is done with the help of the internet. It can't take place without a proper internet connection. Online transactions occur when a process of buying and selling takes place through the internet.
What is a shopping cart?
Solution:
The shopping cart gives a record of all the items selected by the buyer to be purchased, the number of units or quantity desired to be bought per item selected, and the price for each item.
What is digital cash?
Solution:
Digital Cash is a form of electronic currency that exists only in cyberspace and has no real physical properties, but offers the ability to use real currency in an electronic format.
What is BPO?
Solution:
Business process outsourcing or BPO is a business practice in which one organization hires another company to perform a task (process) that the hiring organization requires to operate its own business successfully.
What is KPO?
Solution:
KPO is the sub-segment of BPO, in which the outsource service provider is hired not only for its capacity to perform a particular business process or function but also to provide expertise around it.
What is LPO?
Solution:
LPO is a type of KPO that is specific to legal services, ranging from drafting legal documents, performing legal research to offering advice.
Correct the underlined word and rewrite the following sentence.
E-business is hard to start.
Solution:
E-business is easy to start.
There are five stages of online transactions.
Solution:
There are three stages of online transactions.
Registration is the Last step in online transactions.
Solution:
Registration is the first step in online transactions.
Digital cash is a form of plastic currency.
Solution:
Digital cash is a form of Electronic currency.
KPO includes less knowledge-based and specialized work.
Solution:
KPO includes more knowledge-based and specialized work.
Arrange in proper order.
Purchase or sale / Delivery stage / Pre-purchase or sale.
Solution:
Pre-purchase /sale ,Purchase/sale,Delivery stage
Placing orders, Cash on delivery, Registration
Solution:
Registration, Placing an order, Cash on delivery
Explain the following term/concept.
E-business
Solution:
The term 'E-business' i.e electronic business is derived from the terms of e-mail and e-commerce.
E-business or electronic business is the administration of conducting business via the internet.
This would include the buying and selling of goods or services, along with providing technical or customer support through the internet.
B2B
Solution:
B2B is an acronym for Business to Business, as the name signifies, it is a type of commercial transaction where the purchasing and selling of merchandise are performed between two business houses, such as an entity supplying material to another for production, or an entity providing services to another.
B2C
Solution:
B2C transactions have business firms at one end and its customers on the other end.
The transactions under B2C are between business firms and consumers. Firms use their sites for a range of marketing activities.
C2C
Solution:
Consumer to consumer (C2C) involves the electronically facilitated transactions between consumers through some third party. Common consumers post an item for sale and other consumers bid to purchase it. The sites are only intermediaries, just to match the consumers.
Outsourcing
Solution:
Outsourcing is the process of contracting some business functions to specialized agencies. The company benefits in two ways.
1. It reduces its own cost
2. It uses the expertise of the firm which specializes in a particular kind of service.
BPO
Solution:
BPO is a subset of outsourcing that involves the contracting of the operations and responsibilities of a specific business process to a third-party service provider. BPO refers to the outsourcing of peripheral activities of the organization to an external organization to minimize cost and increase efficiency.
LPO
Solution:
LPO is a type of KPO that is specific to legal services, ranging from drafting legal documents, performing legal research to offering advice. LPO refers to the practice of a law firm or corporation obtaining legal support services from an outside law firm or legal support services company. LPO is a high-end industry that has been growing rapidly in recent years.
KPO
Solution:
KPO is the sub-segment of BPO, in which the outsource service provider is hired not only for its capacity to perform a particular business process or function but also to provide expertise around it.
KPO is a form of outsourcing, in which knowledge-related and information-related work is carried out by workers in a different company or by a subsidiary of the same organization. Which may be in the same country or in an off share location to save cost.
Study the following case/situation and express your opinion.
Abhay purchases some gift articles online from www.flipkart.com. At the same time, Sheetal purchased a gift from e-bay.com.
i. Which website is related to C2C?
ii. Which website is related to B2C?
iii. What first step does Abhay need to follow?
Solution:
eBay.com website is related to Consumer to Consumer (C2C).
www.flipkart.com website is related to Business to Consumer (B2C).
Before online shopping. Abhay has to register with the www.flipkart.com by filling up a registration form. Registration is the first step in online transactions. Abhay needs to login a particular website to buy particular gift articles.
Satvik purchases a watch from Titan shop and his friend Shambhavi purchases a watch from online shopping sites.
i. Which shopping is from a traditional business?
ii. Which shopping is from e-business?
iii. Which business involved high risk?
Solution:
The purchase of a watch by Satvik from Titan shop is an example of traditional business.
The purchase of a watch by Shambhavi from an online shopping site is an example of e-business.
e-business i.e. purchase of a watch from online shopping sites involves high risk as there is no direct contact between Shambhavi and the e-business owners.
Mr. Ved made his payment by cheque at the same time Mr. Shlok made his payment by fund transfer.
i. Whose payment is faster?
ii. Whose payment is related to traditional business?
iii. Whose payment is related to e-business?
Solution:
The payment made by Mr. Shlok by fund transfer is faster than the payment made by Mr. Ved through cheque.
The payment made by Mr. Ved by cheque is related to traditional business.
The payment made by Mr. Shlok by fund transfer is related to e-business.
Distinguish between.
Traditional business and E-business.
E-business and E-commerce
BPO and KPO
Answer in brief
What is outsourcing? Illustrate with suitable examples.
Solution:
Outsourcing is the process of contracting a business function or any specific business activity to specialized agencies mostly the non-core areas such as sanitation, security, household pantry, etc. are outsourced by the company. The company makes a formal agreement with the agency.
Company benefits in two ways.
1. It reduces its own cost
2. It uses the expertise of the firm which specializes in a particular kind of service.
Examples of outsourcing:
The establishments such as shops, malls, housing societies, offices, etc. outsource facilities like canteen, sanitation, security, etc. In the same way arrangements for the wedding, anniversary, birthday celebration can also be outsourced.
What is BPO? Explain in detail?
Solution:
Business process outsourcing or BPO is a business practice in which one organization hires another company to perform a task ( process) that the hiring organization requires to operate its own business successfully.
Meaning:
BPO is a subset of outsourcing that involves the contracting of the operations and responsibilities of a specific business process to a third-party service provider. BPO refers to the outsourcing of peripheral activities of the organization to an external organization to minimize cost and increase efficiency.
BPO refers to the outsourcing of peripheral activities of the organization to an external organization to minimize cost and to increase efficiency. For example, customer care centers for various banks, service providers, etc.
What is KPO? Explain in detail.
Solution:
KPO is described as the functions related to knowledge and information outsourced to third-party service providers.
KPO is the sub-segment of BPO, in which the outsource service provider is hired not only for its capacity to perform a particular business process or function but also to provide expertise around it.
KPO is a form of outsourcing, in which knowledge-related and information-related work is carried out by workers in a different company or by a subsidiary of the same organization. Which may be in the same country or in an off share location to save cost.
KPO requires advanced analytical and technical skills as well as a high degree of specialist expertise. KPO allows both core and non-core activities.
What is LPO? Explain in detail.
Solution:
LPO is a type of KPO that is specific to legal services, ranging from drafting legal documents, Performing legal research to offering advice.
LPO refers to the practice of a law firm or corporation obtaining legal support services from an outside law firm or legal support services company. LPO is the industry in which in-house legal departments or organizations outsource legal work to such areas where it can be done at less cost.
For example, areas like the US or Europe outsourced legal work to India, where it can be performed at a significantly decreased cost. LPO is a high-end industry that has been growing rapidly in recent Years.
Legal outsourcing has gained tremendous ground in the past few years in India. It achieved Success by producing services such as document review, legal research, and writing, drafting of briefings, etc.
Justify the following statement.
It is easy to set up e-business as compared to traditional business.
Solution:
(1) e-business is run, managed, and carried out with the help of information technology, i.e. web (internet). However, traditional business is run, managed, and carried out in accordance with specific old custom or trading practices of long-lasting.
(2) In traditional business large, physical space is needed, to arrange and display a variety of goods. It needs a large amount of capital to have the infrastructure, staff, and other required facilities. e-business can be started, managed, and operated with the help of the internet from any place or even from one's own home. Naturally, it requires very little capital. It is also easy to set up.
(3) In traditional business, time is required to travel, to convince, to negotiate, and to interact with the customers. In such a process a lot of time, energy, and money are wasted. While in e-business required information is provided and accepted with terms and conditions more instantly.
(4) e-business is also free from most of the problems faced by traditional businesses. Thus, it is easy to set up an e-business.
E-business allows users to work across the globe in any field.
Solution:
(1) e-business i.e. electronic business may be defined as the application of information and technologies to support all the activities of the business. It involves electronic buying and supply, chain management, process orders electronically, online payments via debit or credit cards, handling customer service, etc.
(2) In order to begin with e-business, a business owner must have an internet presence. He has to obtain an e-mail address for communicating the same to the customers and other business associates. This helps in speedy communication between business firms and customers.
Communication is easy as there is no face to face interaction.
(3) Once the owner of e-business has acquired an electronic means of contact, he may sell goods to the customers residing in any part of the world. There is no need for any wholesalers, retailers, etc. This reduces costs and increases profit. In e-business, goods can be purchased on the internet from any place across the globe, payments can be made with the help of debt, credit card, internet banking, and the goods are physically delivered at the doorstep of the buyer.
(4) Similarly, he can do trading in any field. e-business uses the internet to connect people and processes. The World Wide Web (WWW) offers a lot of exposure to e-business on a global platform. The international relationship is very strong in e-business. The Government also offers a lot of support to e-business. Thus, it allows one to work across the globe in any field he likes.
Online transactions are done with the help of the internet.
Solution:
(1) Online transactions take place when a process of buying and selling is completed through the internet. For online transactions, registration is required. The consumer needs to login to a particular website to buy a particular article or service. The customer's email ID, name, address, and other details are saved and safe with the website for further contact.
(2) When a customer likes a product or service, he/she selects pickups and drops the items or things in the shopping cart. The shopping cart keeps a systematic and detailed record of what items have been picked up while browsing the online store.
(3) The buyer then proceeds to the payment option after selecting all the products. Payment can be made by accepting cash on delivery mode of payment, after receiving the physical delivery of goods. The customer may pay in cash or by debit or credit card. The buyer also sends a cheque to the seller and the seller sends the products after the realization of the cheque.
(4) If the payment is transferred by the buyer from his account to the seller's account electronically, then after the payment is received by the seller, he sends the goods to the buyer. The credit card or debit card is also used by the cardholder for making payment of purchases. The amount gets immediately transferred to the vendor's bank account. After the successful transfer of funds, goods are delivered by the vendor to the buyer. Thus, all aspects of online transactions are completed with the help of the internet.
Attempt the following.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of e-business?
Solution:
Advantages of e-commerce are as follows:
1) Ease of formation:
The formation of a traditional business is difficult, whereas to form e-business is relatively easy to start.
2) Lower Investment requirements:
The investment requirement is low as compared to traditional business as the store does not have physical existence and can be managed with less manpower so if the trade does not have much of the investment but have contact (network), he can do fabulous business.
3) Convenience:
The Internet offers the convenience of 24 X 7 X 365 days a year. Business is going on at any time and flexibility is available. Yes, e-business is truly a business that has been enabled and enhanced by electronics and offers the advantage of accessing anything, anywhere, any time.
4) Speed:
This benefit becomes all the more attractive when it comes to information. Much of the buying or selling involves the exchange of information that the internet allows at the click of a mouse.
5) Global access:
The Internet is true without boundaries. On one hand, it allows the seller access to the global market. On the other hand, it offers the freedom to the buyer to choose products from almost any part of the world. No need for face to face interaction between buyer and seller.
6) The movement towards a paperless society:
The use of the internet has considerably reduced the dependence on paperwork. Thus, recording and referencing of information has become easy.
7) Government support:
The government provides a favorable environment for setting up of e-business. This support ensures maximum transparency.
8) Easy payment:
The payment in e-business is done by credit card, fund transfer, etc. and it is available round the clock..
The Disadvantages of e-business are a follows:
(1) Lack of personal Touch:
E-business lacks a personal touch. One cannot touch or feel the products. So it is difficult for the consumers to check the quality of products.
(2) Delivery Time:
The delivery of the products takes time. In a traditional business, you get the product as soon as you buy it. But that doesn't happen in online business. This time lag often discourages customers e.g. Amazon now assures one-day delivery. This is an improvement but does not resolve the issue completely.
(3) Security issues:
There are a lot of people who scam through online business. Also, it is easier for hackers to get your financial details. It has a few security and integrity issues. This also causes disturbance among potential customers.
(4) Government interference:
Sometimes the Government monitoring can lead to interference in the business.
(5) High Risk:
High Risk is involved as there is no direct contact between the parties. In the case of fraud, it becomes difficult to take legal action.
What are the types of e-business? Explain.
Solution:
The followings are the types of business:
1) Business to Business (B2B)
2) Business to Consumer (B2C)
3) Consumer to Business (C2B)
4) Consumer to Consumer (C2C)
5) Business to Administration (B2A)
6) Consumer to Administration (C2A)
1) Business to Business (B2B)
In this form, the buyer and seller are both business entities and do not involve individual consumers. Here, both the parties involved in e-commerce transactions are business firms and hence the name B2B i.e. business to business.
Transactions between business firms come under this category. Business firms interact with each other for a variety of services.
2) Business to Consumer (B2C):
B2C transactions have business firms at one end and its customers on the other end.
The transactions under B2C are between business firms and consumers. Firms use their sites for a range of marketing activities. The cost of products and services is kept low through this method and the speed of transactions is also faster.
3) Consumer to Business (C2B)
In this electronic transaction, the consumer requests a specific service from the business. Consumer to Business is a growing arena where the consumer requests a specific service from the business. It enables buyers to quote their own prices for specific goods or services. A consumer posts his request with a set budget online and, companies review the customers’ requirements and bids out the project. For example, pest control services, taxi services, doorstep food delivery, etc.
4) Consumer to consumer (C2C)
It facilitates the online transaction of goods or services between two people. Consumer to consumer (C2 C) involves the electronically facilitated transactions between consumers through a third party. Common consumer posts an item for sale and other consumers bid to purchase it. The sites are only intermediaries, just to match the consumers.
5) Business to Administration (B2A)
This part of e-commerce encompasses all transactions conducted online between business and public administration. For example, registration of companies, payment of taxes, getting permits, etc.
6) Consumer to Administration (C2A)
The consumer to Administration model encompasses all electronic transactions conducted between individuals and public administration. For example, getting a passport, aadhaar card, licenses etc.
What are the advantages of outsourcing?
Solution:
Advantages of Outsourcing:
1) Overall cost advantages -
It reduces the cost and also saves time and effort on training costs.
2) Stimulates entrepreneurship, employment, and exports-
Outsourcing stimulates entrepreneurship, employment, and exports in the country.
3) Low manpower Cost-
The manpower cost is much lower than that of the host company.
4) Access to professional, expert, and high-Quality services-
Mostly the tasks are given to people who are skilled in that particular field. This provides us with a better level of service and fewer chances of errors.
5) Emphasis on core process rather than the supporting ones-
With its help companies can focus on their core areas which lead to better profits and increase the quality of their products.
6) Investment requirements are reduced -
The organization can save on investing in the latest technology, software, and infrastructure and let the outsourcing partner handle the entire infrastructure.
7) Increased efficiency and productivity -
There is increased efficiency and productivity in the non-core areas of an organization.
8) Knowledge sharing -
Outsourcing enables the organization to share knowledge and best practices with each other, it helps develop both the companies and also boosts goodwill in the industry.
What are the disadvantages of outsourcing?
Solution:
Disadvantages of Outsourcing/Limitations of Outsourcing
1) Lack of customer focus-
An outsourced vendor may be catering to the needs of multiple organizations at a time. In such a situation, he may lack complete focus on an individual organization.
As a result, the organization may suffer.
2) A threat to security and confidentiality -
The confidential information of the organization may be leaked to the third party, so there are security issues.
3) Dissatisfactory services -
Some of the common problem areas with outsourcing include stretched delivery time and substandard quality.
4) Ethical issues -
The major ethical issue is taking away employment opportunities from one's own country when the function is outsourced to a company from another country.
5) Other disadvantages -
i) Misunderstanding of the contracts.
ii) Lack of communication.
iii) Poor quality and delayed services.
Answer the following.
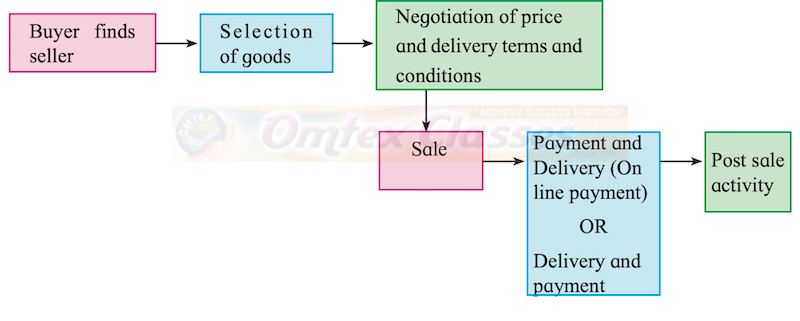
Explain the steps involved in online transactions.
Solution:
The online transaction moves through pre-purchase/sale, actual purchase/sale, and delivery stage. It involves the following steps.
1) Registration -
Before online shopping one has to register with the online vendor by filling up a registration form. Registration is the first step in online transactions. For online transactions, registration is required. The consumer needs to login a particular website to buy a particular article or service. The customer's email ID, name, address, other details are saved and are safe with the website. For security reasons, the buyer's 'Account' and his 'Shopping Cart' is an online record of what you have picked up while browsing the online store.
2) Placing an Order-
It is the second step in online transactions. When a customer likes a product or service he/she puts the product in the shopping cart. The shopping cart gives a record of all the items selected by the buyer to be purchased, the number of units or quantity desired to be bought per item selected, and the price for each item. The buyer then proceeds to the payment option after selecting all the products.
3) Payment -
It is the last step in an online transaction. The buyer has to select the payment option.
These payment systems are secured with very high-level encryption. Personal financial information is completely secure. The following are some ways in which we can make this payment.
a) Cash on Delivery-
In this type of payment, the buyer pays when he/she receives the product. The payment is made at the doorstep. The customer can pay in cash or by debit or credit card.
b) Cheque-
In this type of payment, the buyer sends a cheque to the seller and the seller sends the product after the realization of the cheque.
c) Net Banking transfer-
In this type of payment, the payment is transferred from the buyer's account to the seller's account electronically. After the payment is received by the seller, the seller dispatches the goods to the buyer. It is an electronic facility of transferring funds through the internet.
d) Credit or Debit card -
The buyer makes payment through debit or credit card and the amount gets deducted from customers' accounts. A debit card or credit card popularly known as "Plastic Money". They are mostly used for online payments.
e) Digital Cash -
Digital Cash is a form of electronic currency that exists only in cyberspace and has no real physical properties, but offers the ability to use real currency in an electronic format.
What is outsourcing? Explain the advantages and disadvantages of outsourcing.
Solution:
Outsourcing is the process of contracting some business functions to specialized agencies. The company benefits in two ways.
1. It reduces its own cost
2. It uses the expertise of the firm which specializes in a particular kind of service.
Advantages of Outsourcing:
1) Overall cost advantages-
It reduces the cost and also saves time and effort on training costs.
2) Stimulates entrepreneurship, employment, and exports-
Outsourcing stimulates entrepreneurship, employment, and exports in the country.
3) Low manpower Cost-
The manpower cost is much lower than that of the host company.
4) Access to professional, expert, and high-Quality services-
Mostly the tasks are given to people who are skilled in that particular field. This provides us with a better level of service and fewer chances of errors.
5) Emphasis on core process rather than the supporting ones-
With its help companies can focus on their core areas which lead to better profits and increase the quality of their products.
6) Investment requirements are reduced -
The organization can save on investing in the latest technology, software, and infrastructure and let the outsourcing partner handle the entire infrastructure.
7) Increased efficiency and productivity -
There is increased efficiency and productivity in the non-core areas of an organization.
8) Knowledge sharing -
Outsourcing enables the organization to share knowledge and best practices with each other, it helps develop both the companies and also boosts goodwill in the industry.
Disadvantages of Outsourcing / Limitations of Outsourcing
1) Lack of customer focus-
An outsourced vendor may be catering to the needs of multiple organizations at a time. In such a situation, he may lack complete focus on an individual organization.
As a result, the organization may suffer.
2) A threat to security and confidentiality -
The confidential information of the organization may be leaked to the third party, so there are security issues.
3) Dissatisfactory services -
Some of the common problem areas with outsourcing include stretched delivery time and substandard quality.
4) Ethical issues -
The major ethical issue is taking away employment opportunities from one's own country when the function is outsourced to a company from another country.
5) Other disadvantages -
i) Misunderstanding of the contracts.
ii) Lack of communication.
iii) Poor quality and delayed services.