Activity 1.1 (Write your Own Answer)
- You
all must have been to a shopping mall or a grocery store near your house.
Have you observed how the items are stored in the shelves or counters? Is
there a particular pattern in which they are kept?
- In
your house, your mother often asks you to keep your books, clothes and
other things in order. How do you arrange them so that you can retrieve
them easily when you require them?
- Go
to your school library. Observe how the books are arranged. Ask your
librarian whether any particular method of classification is adopted.
You all know that
matter can exist in the form of elements, compounds and mixtures. When elements
were discovered, scientists adopted different ways to classify them. In earlier
days, very few elements were known. At that time, they were classified as
metals and non-metals on the basis of their properties. Some elements showed
properties of both metals and non-metals and they could not be placed in any of
the two classes. To overcome these difficulties, scientists tried to find out
some pattern or regularity in the properties of elements.
1.1
Dobereiner’s Triads
Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner, a
German scientist (1780 – 1849) studied as a pharmacist at Munchberg in Germany
and then studied chemistry at Strasbourg. He later became professor of
chemistry and pharmacy at the University of Jena.
In 1829, he found
some groups of three elements which showed similar properties. These groups
were called as triads. In these triads, atomic mass of the middle element was
approximately the mean of atomic masses of other two elements. Also these
elements showed similarities in properties. The table below shows four triads
arranged vertically.
Table 1.1
|
Element
|
Atomic Mass
|
Lithium (Li)
|
6.9
|
Sodium (Na)
|
23
|
Potassium (K)
|
39
|
Calcium (Ca)
|
40.1
|
Strontium (Sr)
|
87.6
|
Barium (Ba)
|
137.3
|
Chlorine (Cl)
|
35.5
|
Bromine (Br)
|
79.9
|
Iodine (I)
|
126.9
|
Sulphur (S)
|
32
|
Selenium (Se)
|
79
|
Tellurium (Te)
|
128
|
In the above table, take the triad of Lithium, Sodium and Potassium. The atomic
mass of Sodium (23) is the mean of the atomic masses of Lithium and Potassium.
Similarly, you can verify the atomic
masses of Strontium, Bromine and Selenium from the other triads.
The triads
were known as Dobereiner’s
triads.
Dobereiner could identify
only some triads from the elements known. Other triads did not obey
Dobereiner’s rule. Hence the system of triads was not useful.
1.2
Newlands’ Octaves
|
Newlands
|
British chemist Newlands (1837 – 1898) was born in London and
studied at Royal college of chemistry. He set up a practice as an analytical
chemist in 1864 and in 1868 became chief chemist in a sugar refinery. Later
he left the refinery and worked as an analyst.
|
After the failure of Dobereiner’s triads, the next attempt to classify elements
was done by Newlands. By this time 56 elements
were discovered. Newlands arranged all these elements in increasing order of
their atomic masses. He found that every eighth element had properties similar
to that of the first. He compared this to the octave found in music. Therefore
his classification was known as “Newlands’ Octaves”.
Newlands’ law
states that “When the elements are arranged in an increasing order of their
atomic masses, the properties of the eighth element are similar to the first”.
Table 1.2
H
|
Li
|
Be
|
B
|
C
|
N
|
O
|
F
|
Na
|
Mg
|
Al
|
Si
|
P
|
S
|
Cl
|
K
|
Ca
|
Cr
|
Ti
|
Mn
|
Fe
|
Some
features of Newlands’ table
- Newland could arrange elements
only up to calcium out of total 56 elements known.
- After calcium every eighth element
did not posses properties similar to that of the first.
- At the time of Newlands only 56
elements were known. But later several elements were discovered.
- In order to fit the existing
elements Newland placed two elements in the same position which differed
in their properties.
- This periodic table did not
include inert (noble) gases because they were not discovered.
Identify
Dobereiner’s triads in Newlands’ table. (Table 1.2) Answer
1.3
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
|
Mendeleev
|
Dimitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist (1834 -1907) was born at
Tobolsk, Siberia. He studied science at St. Petersburg and graduated in 1856.
In 1863, he was appointed to a professorship and in 1866 he succeeded to the
chair in the university.
|
Mendeleev
examined the relationship between the atomic masses of the elements and their
physical and chemical properties. Among chemical properties, he concentrated on
the compounds formed by the elements with oxygen and hydrogen as they were very
reactive and formed compounds with most elements. By analyzing these compounds,
Mendeleev believed that atomic mass of element was the most fundamental
property in classifying the elements. He arranged elements in the increasing
order of their atomic masses and found that the chemical and physical
properties of elements showed repetition after certain intervals. He arranged
known elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses in the horizontal
row still he encountered an element which had properties similar to the first
element. He placed this element below first element and thus started the second
row of elements. Proceeding in this manner, he could arrange all known elements
according to their properties and thus created the first periodic table containing
63 elements known till then.
His law is known as
Mendeleev’s periodic law:
The
physical and chemical properties of elements are a periodic function of their
atomic masses.
The
tabular arrangement of the elements based on the periodic law is called the Mendeleev’s
periodic table.
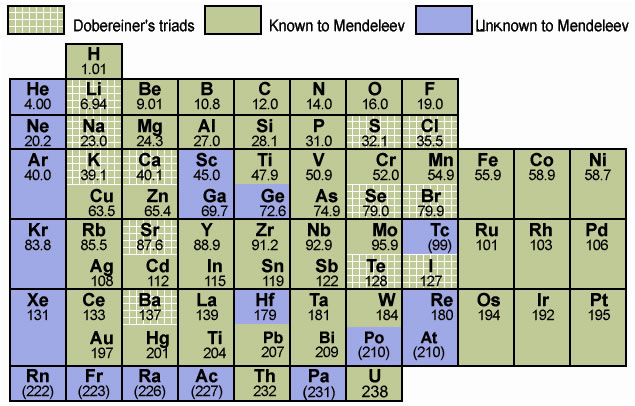
Table 1.3
: Mendeleev's Periodic Table
Table 1.4
: Mendeleev's Periodic Table (with blank spaces)

1.3.1 Main Features of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- The horizontal rows in the periodic table are called periods. There are seven periods. These are numbered from 1 to 7.
- Properties of elements in a particular period show regular gradation from left to right.
- Vertical columns in the periodic table are called groups. There are eight groups numbered from I to VIII. Groups I to VII are further divided into A and B subgroups.
1.3.2 Merits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Mendeleev was the first who successfully classified all known elements.
- Mendeleev kept some blank places in his periodic table. These vacant spaces were for elements that were yet to be discovered. He also predicted properties of these elements even before they were discovered. Later they were found to be correct. (Table 1.5)
- When noble gases were discovered later, they were placed in Mendeleev’s periodic table without disturbing the positions of other elements.
Table 1.5
| Predicted element | Actual element discovered later |
|---|
| Eka-boron | Scandium |
| Eka-aluminum | Gallium |
| Eka-silicon | Germanium |
Table 1.6 : Comparison of properties of eka-aluminium and Gallium
| Eka-aluminium (Ea) | Gallium (Ga) |
|---|
| Atomic weight | About 68 | 69.72 |
| Density of solid | 6.0 g/cm³ | 5.9 g/cm³ |
| Melting point | Low | 29.78ºC |
| Valency | 3 | 3 |
| Method of discovery | Probably from its spectrum | Spectroscopically |
| Oxide | Formula: Ea2O3
Density: 5.5 g/cm³
Soluble in both acids and alkalies | Formula: Ga2O3
Density: 5.88 g/cm³
Soluble in both acids and alkalies |
1.3.3 Demerits of Mendeleev’s periodic Table
- Hydrogen resembles alkali metals as well as halogens. Therefore, no fixed position could be given to hydrogen in the periodic table.
- Isotopes of same elements have different atomic masses; therefore each one of them should be given a different position. On the other hand as isotopes are chemically similar, they had to be given same position.
- At certain places, an element of higher atomic mass has been placed before an element of lower mass. For example, cobalt (Co = 58.93) is placed before nickel (Ni = 58.71).
- Some element placed in the same sub group had different properties. e. g. Manganese (Mn) is placed with halogens which totally differ in the properties.
Activity 1.3 (Answers)
- Consider isotopes of oxygen 16O and 18O. Would you be able to place them in Mendeleev’s periodic table?
- Find resemblance between hydrogen and alkali metals by writing compounds of both with chlorine, sulphur and oxygen.
- Find out a pair of elements from the periodic table where higher mass element is placed before lower mass element.
1.4 Modern Periodic Table
In 1913, Henry Moseley, an English physicist discovered that atomic number is the most fundamental property of an element and not it’s atomic mass. Atomic number (Z) of an element is the number of electrons present in the outer shells. This discovery changed the whole perspective about elements and their properties. Accordingly Mendeleev’s periodic law was modified into ‘Modern periodic Law’.
The modern Periodic Law states “The chemical and physical properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers”.
The periodic table based on modern periodic law is called the Modern Periodic Table. Many version of this periodic table are in use but the one which is most commonly used is Long Form of Modern Periodic Table.
If you look at the Modern Periodic Table, you will observe that it is not much different from Mendeleev’s periodic table.
| Table 1.7 : Modern Periodic Table |
|---|

Activity 1.4 (Answers)
- How are isotopes of different elements placed in the Modern Periodic Table?
- What should be the position of Hydrogen in the Modern Periodic Table?
- Write the name, symbol and electronic configuration of first ten elements.
1.4.1 Position of elements in the Modern Periodic Table
- The horizontal rows in the Modern Periodic Table are called as periods and the vertical columns are called as groups.
- The Modern Periodic Table consists of seven periods and eighteen groups.
- Periods are numbered from 1 to 7. Elements presenting the same period have same number of shells which is equal to the period number.
- In each period a new shell starts filling up. The period number is also the number of shell which starts filling up in it.
- The first period is the shortest period containing only two elements. Second and third periods are called as short periods and fifth periods are long periods and containing 18 elements each. Sixth period is the longest and contains 32 elements in it. Seventh period is an incomplete period.
- Groups are numbered from 1 to 18. Elements having same number of valence electrons or having same outer electronic configuration are present in the same group.
- Elements present in the same group show same chemical properties.
- Group 1 contains alkali meals. Group 2 contain alkaline earth metals. Group 17 contains halogens. Group 18 contains inert gases.
Activity 1.5 (Answers)
- Write the electronic configuration of elements from atomic number 11 to 18.
- What similarities do you find in their electronic configuration?
- How many valence electrons are present in sodium, aluminum and chlorine?
- Write the electronic configuration of (i) Mg and Ca, (ii) F and Cl.
- Do these elements contain same number of valence electrons?
- Write electronic configuration of B, O, Na, Al, S and K.
- Metals are present on the left hand side of the periodic table, whereas non-metals are present on right side of the periodic table.
- Elements present in group 1 and 2 on the left side and 13 to 17 on the right side of the periodic table are normal elements. Their one outermost shell is incomplete.
- Elements present in groups 3 to 12 in the middle of the periodic table are called as transition elements. Their two outermost shells are incomplete.
- Group 18 on the extreme right of the periodic table contains inert gases. Their outermost shell contains 8 electrons.
- Elements placed at the bottom of the periodic table are called as inner transition elements. They contain two series of elements lanthanides and actinides.
- 14 elements with atomic numbers 58 to 71 (Ce to Lu) are called as lanthanides. These elements are placed along with lanthanum (La = 57) in the same group 3 in period 6 because of very close resemblance in properties between them.
- 14 elements with atomic numbers 90 to 103 (Th to Lr) are called as actinides. These elements are placed along with actinium (Ac = 89) in the same group 3 in period 7 because of very close resemblance in properties.
Activity 1.6 (Answers)
- Classify elements from atomic number 11 to 18 as metals and non-metals depending on the electrons present in the outermost shell.
- Write the electronic configuration of Mg, K, Ar and F. Write the electronic configuration of elements from atomic number 11 to 18.
- Elements in the modern periodic table are classified on the basis of their electronic configuration. They are divided into four blocks: s–block, p–block, d–block and f–block.
- Groups 1 and 2 are included in s–block. These elements contain 1 or 2 electrons in their outermost shell. All these elements are metals.
- Groups 13 to 17 and 0 group elements are included in p–block. They contain 3 to 8 electrons in their outermost shell. P–block contains all types of elements, i.e. metals, non–metals and metalloids.
- Elements from s–block and p–block are called as normal elements. These elements have outermost shell incomplete except 0 group elements.
- 0 group elements have completed outermost shell. They are called as inert elements or noble elements. All these elements are gases.
- Groups 3 to 12 are known as d–block elements. These elements have two outermost shells incomplete. They are known as transition elements. All these elements are metals.
- Elements present at the bottom of the periodic table, i.e. lanthanides and actinides are called as f-block elements. They have three incomplete outermost shells. They are called as inner transition elements. All these elements are metals.
Activity 1.7 (Answers)
- Select any 20 elements from all groups.
- Identify the block to which each element belongs.
- Identify the group to which the element belongs.
1.4.2 Merits of Modern periodic Table over Mendeleev’s periodic Table
- All isotopes of the same elements have different masses but same atomic number. Therefore, they occupy the same position in the modern periodic table.
- When elements are arranged according to their atomic numbers the anomaly regarding certain pairs of elements in Mendeleev’s periodic table disappears. e. g. atomic number of Cobalt and Nickel are 27 and 28 respectively. Therefore, Cobalt will come first and then Nickel, although its atomic mass is greater.
- Elements are classified according to their electronic configuration into different blocks.
1.4.3 Periodic Properties:
The properties which show gradual variation in a group and in a period and they repeat themselves after a certain interval of atomic number are called periodic properties.
Activity 1.8 (Answers)
- How do you calculate valency of an element from its electronic configuration?
- What is the valency of elements with atomic number 8, 14, 17 and 20?
- How does valency vary in a period and in a group?
Atomic Size:
Atomic size is determined using atomic radius. For an isolated atom, atomic radius. For an isolated atom, atomic distance is the distance between the centre of atom and the outermost shell. In a period, atomic radius generally decreases from left to right. This is because the electrons are added to same shell and experience greater pull from the nucleus. Atomic radius increases in a group from top to bottom as new shells are added bringing outermost electrons farther from the nucleus.
Activity 1.9 (Answers)
- Atomic radii of elements of third period are given below:
| Period 3 elements : | S | Na | Cl | P | Mg | Si | Al |
|---|
| Atomic radius (pm) : | 127 | 190 | 99 | 128 | 160 | 132 | 143 |
(a) Arrange them in the decreasing order of their atomic radii.
(b) Are they arranged as in the periodic table?
(c) Which are the atoms of highest and lowest atomic radii?
(d) What trend is observed in the atomic radii in a period from left to right?
- Atomic radii of group 17 are given below:
| Group 17 elements : | I | F | Cl | Br |
|---|
| Atomic radius (pm) : | 133 | 72 | 99 | 114 |
(a) Arrange them in the decreasing order of their atomic radii.
(b) Are they arranged as in the periodic table?
(c) Which are the atoms of highest and lowest atomic radii?
(d) What trend is observed in the atomic radii down the group?
Metallic and non-metallic properties:
Metals show tendency to lose electrons. Therefore, they are said to be electropositive. Non-metals show tendency to accept electrons or share electrons with another atom. Therefore, they are said to be electronegative. Metallic character deceases and non-metallic character increases from left to right in a period. This is because atomic size decreases. Therefore, the electrons are all metals and on the right of periodic table in the group, lower members are metals. In a group, metallic character increases and non-metallic character decreases from top to bottom. This is because atomic size increases and valence electrons can be easily removed. In group 14, first element is carbon (C) which is non-metal, next two elements silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge) are metalloids and remaining elements Tin (Sn) and Lead (Pb) are metals. In the modern periodic table, a zig-zag line separates metals from non-metals. The borderline elements i.e. boron (B), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As), Tellurium (Te) and Polonium (Po) show intermediate properties and are called as metalloids or semi-metals.

|