Chapter 2: Solutions
Balbharati solutions for Chemistry 12th Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 2 - Solutions [Latest edition]
Exercise | Q 1.01 | Page 44
Choose the most correct option.
The vapour pressure of a solution containing 2 moles of a solute in 2 moles of water (vapour pressure of pure water = 24 mm Hg) is ______.
Options
24 mm Hg
32 mm Hg
48 mm Hg
12 mm Hg
Solution
The vapour pressure of a solution containing 2 moles of a solute in 2 moles of water (vapour pressure of pure water = 24 mm Hg) is 12 mm Hg.
Exercise | Q 1.02 | Page 44
Choose the most correct option.
The colligative property of a solution is _______.
Options
vapour pressure
boiling point
osmotic pressure
freezing point
Solution
The colligative property of a solution is osmotic pressure.
Exercise | Q 1.03 | Page 44
Choose the most correct option.
In calculating osmotic pressure the concentration of solute is expressed in _______.
Options
molarity
molality
mole fraction
mass percent
Solution
In calculating osmotic pressure the concentration of solute is expressed in molarity.
Exercise | Q 1.04 | Page 44
Choose the most correct option.
Ebullioscopic constant is the boiling point elevation when the concentration of a solution is _______.
Options
1 m
1 M
1 mass %
1-mole fraction of solute.
Solution
Ebullioscopic constant is the boiling point elevation when the concentration of solution is 1 m.
Exercise | Q 1.05 | Page 44
Choose the most correct option.
Cryoscopic constant depends on _______.
Options
nature of solvent
nature of solute
nature of solution
number of solvent molecules
Solution
Cryoscopic constant depends on number of solvent molecules.
Exercise | Q 1.06 | Page 45
Choose the most correct option.
Identify the CORRECT statement.
Options
Vapour pressure of solution is higher than that of pure solvent.
Boiling point of solvent is lower than that of solution.
Osmotic pressure of solution is lower than that of solvent.
Osmosis is a colligative property.
Solution
Boiling point of solvent is lower than that of solution.
Exercise | Q 1.07 | Page 45
Choose the most correct option.
A living cell contains a solution which is isotonic with 0.3 M sugar solution. What osmotic pressure develops when the cell is placed in 0.1 M KCl solution at body temperature?
Options
5.08 atm
2.54 atm
4.92 atm
2.46 atm
Solution
2.54 atm.
Exercise | Q 1.08 | Page 45
Choose the most correct option.
The osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose isotonic with blood has the percentage (by volume)________.
Options
5.41 %
3.54 %
4.53 %
53.4 %
Solution: Click Here to Get the Explained Answer.
Exercise | Q 1.09 | Page 45
Choose the most correct option.
Vapour pressure of a solution is _______.
Options
directly proportional to the mole fraction of the solute
inversely proportional to the mole fraction of the solute
inversely proportional to the mole fraction of the solvent
directly proportional to the mole fraction of the solvent
Solution
Vapour pressure of a solution is inversely proportional to the mole fraction of the solute.
Exercise | Q 1.1 | Page 45
Choose the most correct option.
Pressure cooker reduces cooking time for food because _______.
Options
boiling point of water involved in cooking is increased
heat is more evenly distributed in the cooking space
the higher pressure inside the cooker crushes the food material
cooking involves chemical changes helped by a rise temperature
Solution
Pressure cooker reduces cooking time for food because boiling point of water involved in cooking is increased.
Exercise | Q 1.11 | Page 45
Choose the most correct option.
Henry’s law constant for a gas CH3Br is 0.159 mol dm-3 atm-1 at 25 °C. What is the solubility of CH3Br in water at 25 °C and partial pressure of 0.164 atm?
Options
0.0159 mol L-1
0.164 mol L-1
0.026 M
0.042 M
Solution
0.026 M
Explanation:
S = KHP = 0.159 mol dm-3 atm-1 × 0.164 atm
= 0.026 M
Exercise | Q 1.12 | Page 45
Choose the most correct option.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct for 0.1 M urea solution and 0.05 M sucrose solution?
Options
Osmotic pressure exhibited by urea solution is higher than that exhibited by sucrose solution
Urea solution is hypertonic to sucrose solution
They are isotonic solutions
Sucrose solution is hypotonic to urea solution
Solution
They are isotonic solutions.
Exercise | Q 2.01 | Page 45
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
What is osmotic pressure?
Solution
The hydrostatic pressure (on the side of solution) that stops osmosis is called an osmotic pressure of the solution.
OR
The excess of pressure on the side of the solution that stops the net flow of solvent into the solution through a semipermeable membrane is called osmotic pressure.
Exercise | Q 2.02 | Page 45
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
A solution concentration is expressed in molarity and not in molality while considering osmotic pressure. Why?
Solution
1. The osmotic pressure measurements are made at a specific constant temperature. Molarity remains constant at a specific temperature.
2. It is not necessary to express concentration in a temperature-independent unit like molality.
Hence, the solute concentration is expressed in molarity while calculating osmotic pressure rather than molality.
Exercise | Q 2.03 | Page 45
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
Write the equation relating boiling point elevation to the concentration of the solution.
Solution
The boiling point elevation is directly proportional to the molality of the solution. Thus,
Δ Tb ∝ m
∴ Δ Tb ∝ Kb m
where, m is the molality of solution. The proportionality constant Kb is called boiling point elevation constant or molal elevation constant or ebullioscopic constant.
Exercise | Q 2.04 | Page 45
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
A 0.1 m solution of K2SO4 in water has a freezing point of – 4.3 °C. What is the value of van’t Hoff factor if Kf for water is 1.86 K kg mol–1?
Solution: Click here to get the Answer.
Exercise | Q 2.05 | Page 45
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
What is van’t Hoff factor?
Solution: Click Here for Answer.
Exercise | Q 2.06 | Page 45
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
How is van’t Hoff factor related to degree of ionization?
Solution: Click Here for Answer.
Exercise | Q 2.07 | Page 45
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
Which of the following solution will have higher freezing point depression and why?
i. 0.1 m NaCl
ii. 0.05 m Al2(SO4)3
Solution: Click Here for Answer.
Exercise | Q 2.08 | Page 45
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
State Raoult’s law for a solution containing a nonvolatile solute.
Solution
The Raoult’s law states that, “the vapour pressure of solvent over the solution is equal to the vapour pressure of pure solvent multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution.”
Exercise | Q 2.09 | Page 45
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
What is the effect on the boiling point of water if 1 mole of methyl alcohol is added to 1 dm3 of water? Why?
Solution
i. When 1 mole of methyl alcohol is added to 1 dm3 of water, the boiling point of water decreases.
ii. Methyl alcohol is a volatile liquid. Therefore, it increases the vapour pressure of a solution at a given temperature. Hence, the solution boils at lower temperature.
Exercise | Q 2.1 | Page 45
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
Which of the four colligative properties is most often used for molecular mass determination? Why?
Solution
i. Among the four colligative properties, osmotic pressure is most often used for molecular mass determination.
ii. Osmotic pressure is much larger and therefore more precisely measurable property than other colligative properties.
Therefore, it is useful to determine molar masses of very expensive substances and of the substances that can be prepared in small quantities.
Exercise | Q 3.1 | Page 45
Answer the following.
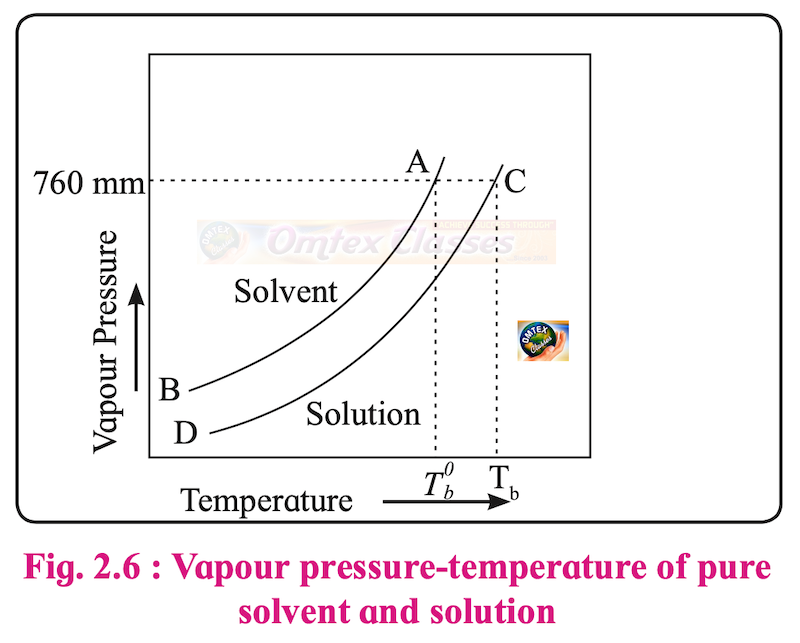
How vapour pressure lowering is related to a rise in the boiling point of solution?
Solution
i. At the boiling point of a liquid, its vapour pressure is equal to 1 atm.
ii. In order to reach boiling point, the solution and solvent must be heated to a temperature at which their respective vapour pressures attain 1 atm.
iii. At any given temperature the vapour pressure of a solution is lower than that of pure solvent. Hence, the vapour pressure of solution needs a higher temperature to reach 1 atm than that of needed for vapour pressure of solvent.
Therefore, vapour pressure lowering causes a rise in the boiling point of a solution.
Exercise | Q 3.2 | Page 45
Answer the following.
What are isotonic and hypertonic solutions?
Solution
i. Isotonic solutions:
Two or more solutions having the same osmotic pressure are said to be isotonic solutions.
e.g. For example, 0.1 M urea solution and 0.1 M sucrose solution are isotonic because their osmotic pressures are equal. Such solutions have the same molar concentrations but different concentrations in g/L. If these solutions are separated by a semipermeable membrane, there is no flow of solvent in either direction.
ii. Hypertonic solution:
If two solutions have unequal osmotic pressures, the more concentrated solution with higher osmotic pressure is said to be the hypertonic solution.
e.g. For example, if osmotic pressure of sucrose solution is higher than that of urea solution, the sucrose solution is hypertonic to urea solution.
Exercise | Q 3.3 | Page 46
Answer the following.
A solvent and its solution containing a nonvolatile solute are separated by a semipermeable membrane. Does the flow of solvent occur in both directions? Comment giving a reason.
Solution
1. When a solution and pure solvent or two solutions of different concentrations are separated by a semipermeable membrane, the solvent molecules pass through the membrane.
2. The passage of solvent molecules through the semipermeable membrane takes place in both directions, since the solvent is on both sides of the membrane.
3. However, the rate of passage of solvent molecules into the solution or from a more dilute solution to more concentrated solution is found to be greater than the rate in the reverse direction.
4. This is favorable since the vapour pressure of solvent is greater than that of solution.
Exercise | Q 3.4 | Page 46
Answer the following.
The osmotic pressure of CaCl2 and urea solutions of the same concentration at the same temperature are respectively 0.605 atm and 0.245 atm, calculate van’t Hoff factor for CaCl2.
Solution: Click Here for Solution
Exercise | Q 3.5 | Page 46
Answer the following.
Explain reverse osmosis.
Solution
i. If a pressure larger than the osmotic pressure is applied to the solution side, then pure solvent from the solution passes into pure solvent side through the semipermeable membrane. This phenomenon is called reverse osmosis.
ii. For example, consider fresh water salt water separated by a semipermeable membrane. When the pressure larger than the osmotic pressure of a solution is applied to solution, pure water from salty water passes into fresh pure water through the membrane. Thus, the direction of osmosis can be reversed by applying a pressure larger than the osmotic pressure.
iii. The schematic set up for reverse osmosis is as follows:
Exercise | Q 3.6 | Page 46
Answer the following.
How molar mass of a solute is determined by osmotic pressure measurement?
Solution: Click Here For Solution.
Exercise | Q 3.7 | Page 46
Answer the following.
Why vapour pressure of a solvent is lowered by dissolving a nonvolatile solute into it?
Solution
i. Vapour pressure of a liquid depends on the ease with which the molecules escape from the surface of the liquid.
ii. When a nonvolatile solute is dissolved in a solvent, some of the surface molecules of the solvent are replaced by nonvolatile solute molecules. These solute molecules do not contribute to vapour above the solution.
iii. Thus, the number of solvent molecules available for vaporization per unit surface area of a solution is less than the number at the surface of the pure solvent.
iv. As a result the solvent molecules at the surface of solution vaporize at a slower rate than pure solvent. This results in lowering of vapour pressure
Exercise | Q 3.8 | Page 46
Answer the following.
Answer the following. Using Raoult’s law, how will you show that ΔP = P10x2? Where, x2 is the mole fraction of solute in the solution and P10 vapour pressure of pure solvent. - Chemistry
Solution: Click Here for Solution.
Exercise | Q 3.9 | Page 46
Answer the following.
While considering boiling point elevation and freezing point depression a solution concentration is expressed in molality and not in molarity. Why?
Solution
1. In boiling point elevation and freezing point depression, we deal with the systems whose temperature is not constant.
2. We cannot express the concentration of the solution in molarity because it changes with temperature whereas molality is temperature independent.
Hence, while considering boiling point elevation and freezing point depression a solution concentration is expressed in molality and not in molarity.
Exercise | Q 4 | Page 46
Derive the relationship between the degree of dissociation of an electrolyte and van’t Hoff factor.
Solution: Click Here for Solution
Exercise | Q 5 | Page 46
What is the effect of temperature on solubility of solids in water? Give examples.
Solution
1. The effect of temperature on solubility of a substance depends on enthalpy of solution.
a. When the substance dissolves in water by an endothermic process, that is, with the absorption of heat, its solubility increases with an increase of temperature.
e.g. KCl dissolve in water by endothermic process.
b. On the other hand, when the substance dissolves in water by an exothermic process, that is, with the release of heat, its solubility decreases with an increase of temperature.
e.g. CaCl2 and Li2SO4.H2O dissolve in water releasing heat.
2. It is important to understand that there is no direct correlation between solubility and exothermicity or endothermicity. For example, dissolution of CaCl2 in water is exothermic and that of NH4NO3 is endothermic. However, the solubility of these substances increases with the temperature